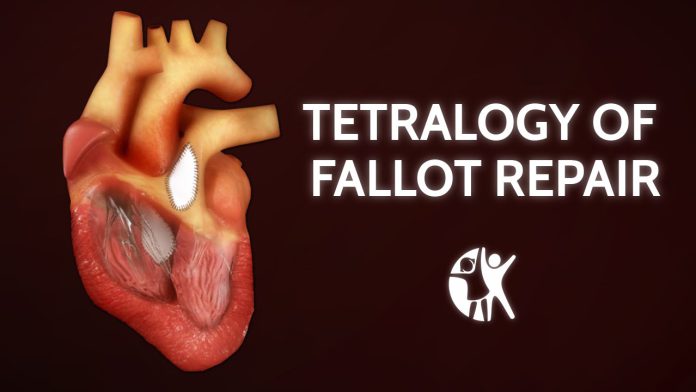
Exproperti.com – Surgery can correct the abnormalities that cause Tetralogy of Fallot. There are two types of surgery for this condition. The shunt surgery corrects one abnormality and gives more blood to the lungs. The other type of surgery corrects the two main abnormalities. Some patients have one or both surgeries in their lifetime. In this article, we’ll examine the pros and cons of each. This information will help you make an informed decision about the type of surgery for your case.
The only way to definitively diagnose tetralogy is via cardiac catheterization
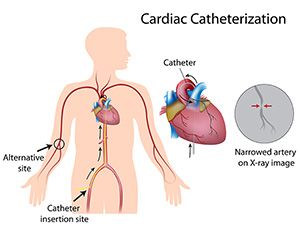
A cardiac catheterization is the first step in determining whether a patient has Tetralogy of Fallot. This invasive procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. Before the discovery of echocardiography, this procedure was performed on patients with suspected tetralogy. Before this test, the only way to definitively diagnose tetralogy was through the cardiac catheterization. A small tube is inserted into a blood vessel in the groin, and advanced up the inferior vena cava. Infusing a dye into the tube highlights a variety of tetralogy symptoms, including a ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, and an abnormal aorta.
Infants with tetralogy of Fallot may experience episodes of severe cyanosis and breathing difficulty. Some may be restless and nonresponsive to their parents’ voices. Severe attacks may result in the infant passing out. Symptoms of a severe attack include a loss of consciousness, convulsions, and temporary paralysis of one side of the body. These spells can last anywhere from minutes to hours. Once they’re over, an infant with Tetralogy of Fallot will go into prolonged sleep.
Fallot’s tetralogy surgery aims to correct defects in the heart
Surgery for tetralogy of Fallot is performed by a team of cardiac surgeons before the infant reaches one year of age. The surgery aims to repair the defects in the heart that prevent oxygen-poor blood from reaching the lungs. The ventricular septal defect is repaired with a patch and the obstructed pathway between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery is opened. Sometimes, the pulmonary valve is also opened.
Children with tetralogy of Fallot will need lifelong care from a cardiologist. Until they reach adulthood, pediatric cardiologists will closely monitor them and coordinate their care with their primary care physician. While they don’t need to see a cardiologist every day, it’s important to follow their doctor’s advice. The Philadelphia Adult Congenital Heart Center specializes in treating patients with Tetralogy of Fallot.
Early examination is very important for the health of children

Early detection of tetralogy of Fallot is crucial for the health of your child. Your doctor may perform an ultrasound exam during pregnancy. Other diagnostic procedures may include a fetal echocardiogram to evaluate the child’s heart structure and function. A chest x-ray is also done to assess the size of the heart and its relationships with other organs in the child’s chest. A catheter is also inserted into the child’s bloodstream and guided into the heart.
The causes of tetralogy of fallot are still unknown. It is thought that it is a complex interaction of various genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Research has shown that the condition is more common in women who have had multiple pregnancies and has a genetic link to maternal alcohol abuse. Other causes include pregnancy after 40, poor nutrition, and certain medications used by the mother. Although not entirely clear, tetralogy of fallot affects approximately 25 percent of infants.
People with tetralogy of Fallot should seek medical attention as early as possible
During the development of a fetal heart, tetralogy of fallot results in a heart structure that does not separate properly. The heart does not pump enough blood to the lungs. It also causes the skin to turn blue. People with tetralogy of fallot should seek medical attention as early as possible. If your child is diagnosed with the disorder, your pediatrician will be able to determine the exact type of surgery that will best suit their needs.
Although most patients with tetralogy of fallot will survive until adulthood, there is an increased risk of pulmonary valve regurgitation. They may also develop heart rhythm abnormalities and require surgery to repair the pulmonary valve. If you suspect your child has this condition, you should consult a pediatric cardiologist or an adult congenital heart specialist. If your child is suffering from tetralogy of fallot, the best way to treat it is to start early with surgery.